What is Data Governance?
Data Governance is simply the practice of applying formal accountability and behaviour to assure quality, effective use, compliance, security and protection of data. In alignment with the strategic priorities of the University of British Columbia, the Data Governance Program creates the foundation to enable students, faculty and staff to make data driven decisions with measurable outcomes.
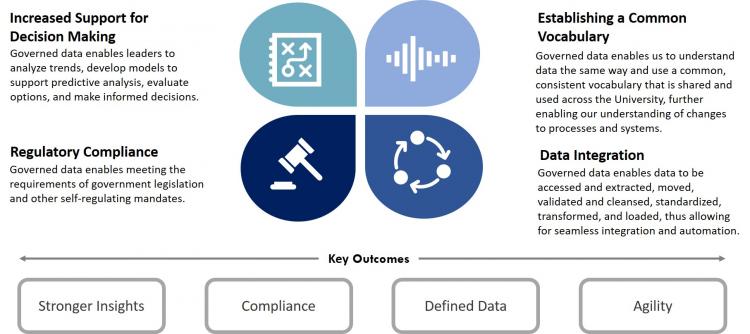
Benefits
The primary benefit of Data Governance is the enablement to derive value from data assets.
The Governance and Management of Data
The purpose of Data Governance is to ensure that data is managed properly, following policies and best practices, and that data decisions are made based on University needs.
Data management is the execution, and supervision of plans, policies, programs, and practices that deliver, control, protect, and enhance the value of data and information assets throughout their lifecycle. Data Governance provides a framework, direction, and oversight for data management to engage and align with the University's priorities and stakeholders over the lifecycle of data.
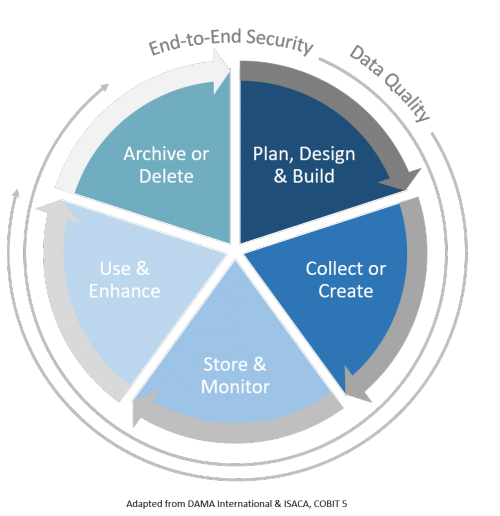
Lifecycle Management of Data
To effectively manage data assets, we need to understand and plan for the data lifecycle. Data is complex. By applying a lifecycle perspective, it assists with simplifying the complexity to plan and strategize the management of data.
It is important to note that despite the linear representation of the lifecycle of data, it is usually not the case. Throughout its lifecycle, data may be cleansed, transformed, merged, enhanced, or aggregated. As data is used or enhanced, new data is often created, thus internal iterations are not represented in the lifecycle.
| Plan, Design & Build |
Before collecting or creating data, a comprehensive plan is required to gather requirements. This will inform the design and build of the solution, and data management needs. |
| Collect or Create |
The collection and creation of data needs to adhere to privacy laws, such that collection of personal information is authorized. Additionally, consideration for applicable data standards, and guidelines are required to ensure data consistency and quality from the time it enters a system. |
| Store & Monitor |
After data is collected or created, it must be stored and monitored, such that it meets regulatory requirements (data residency laws applied to personal information), and to ensure the availability and quality of data. |
| Use & Enhance | Data is meant to be accessed and used, but its purpose and usage need to be aligned, and reflected in the access / security controls. |
| Archive or Delete | At the end of its lifecycle, data needs to be archived and deleted in accordance with approved retention schedules that balance business needs, legal requirements, and risk. |
| Data Quality | The quality of data needs to be monitored at all stages of the data lifecycle. |
| Data Security | Data must be secured and protected at all stages of the data lifecycle. |
Data Management Framework
Given the complexities of managing data throughout its lifecycle, there are various industry approaches involving different levels of abstraction on how to manage data. UBC Enterprise Data Governance has adopted the International Data Management Association's (DAMA) framework. The DAMA framework includes a set of interdependent functions, each with its own goals, activities, and responsibilities. It should be noted that not all functions are applicable to every organization, and that they need to be prioritized in alignment with the strategic direction of an organization.
| Data Architecture |
Enterprise data models, tool standards, and system naming conventions |
|
Data Modelling and Design |
Data model management procedures, data modeling naming conventions, definition standards, standard domains, and standard abbreviations |
| Data Storage and Operations |
Tool standards, database recovery and business continuity, database performance, data retention, and external data acquisition |
| Data Security |
Data access security standards, monitoring and audit procedures, storage security standards, and training requirements |
| Data Integration |
Standard methods and tools used for data integration and interoperability |
| Documents and Content |
Content management standards and procedures, including use of enterprise taxonomies, support for legal discovery, document and email retention periods, electronic signatures, and report distribution approaches |
| Reference and Master Data |
Reference Data Management control procedures, systems of data record, assertions establishing and mandating use, standards for entity resolution |
| Data Warehousing and Business Intelligence |
Tool standard, processing standards and procedures, report and visualization formatting standards, standards for Big Data handling |
| Metadata |
Standard business and technical Metadata to be captured, Metadata integration procedures and usage |
| Data Quality |
Data quality rules, standard measurement methodologies, data remediation standards and procedures |