Data Quality can be defined as the degree to which data is accurate, complete, timely, consistent with all requirements and business rules, and relevant for a given use.
There are three parts to understanding and working towards quality data:
- Proactive data management
- Understanding and defining data quality dimension
- Data quality improvement framework
Data Quality Dimensions
| Data Quality Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Completeness | The degree to which data is populated based on the business rules that state when data is required to be populated with a value. |
| Uniqueness | The degree to which data is allowed to have duplicate values. |
| Consistency | The degree to which data conforms to rule. |
| Conformity | The degree to which data conforms to the business rules for acceptable content, such as format, reference data, standards, and data type. |
| Integrity | The degree to which data elements contain consistent across multiple data bases. |
| Timeliness | The degree to which changes to the data are available within the timeframe required by business. |
| Coverage | The degree to which data supports all business functions that need the data to perform business processes. |
| Accuracy | The degree to which the data corresponds to known correct values in the real world, as provided by a recognized or established source of truth. |
Data Quality Improvement Framework
Given the volume of data and resource restraints, data elements should be prioritized for data quality monitoring and improvement. Data quality improvement has a lifecycle and it can be defined in five phases which include a set of sub processes for consideration:
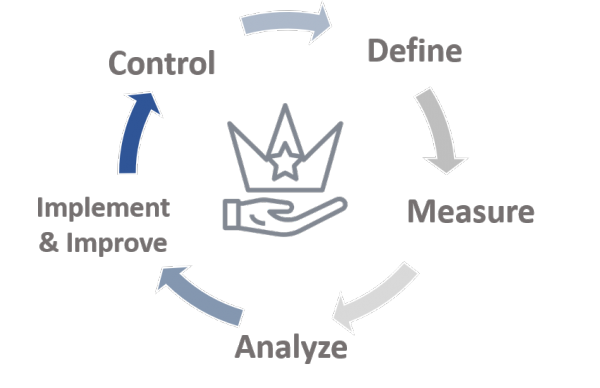
| Phase | Sub-process |
|---|---|
| Define |
|
| Measure |
|
| Analyze |
|
| Improve and implement |
|
| Control |
|