The purpose of Data Governance is to move data from an ungoverned state to a governed state. Ungoverned data refers to data that is rarely defined, has unknown quality, vague or conflicting business rules, and no accountability. Governed data is data that is trusted and understood. Someone is accountable for both the data itself and the issues that need to be addressed about the data.
In addition, governed data means that the University has defined, approved, and documented the following at the data element level:
- Standardized business name and definition of the data element
- Representation in the University Data Model
- Reference data
- Calculation or derivation rule, if applicable
- The Data Trustee and Data Steward for the data element
Given the large volume of data elements across the University, we need to prioritize the most important business data elements to focus on, such as financial reporting data, or compliance and regulatory data.
Data Modelling
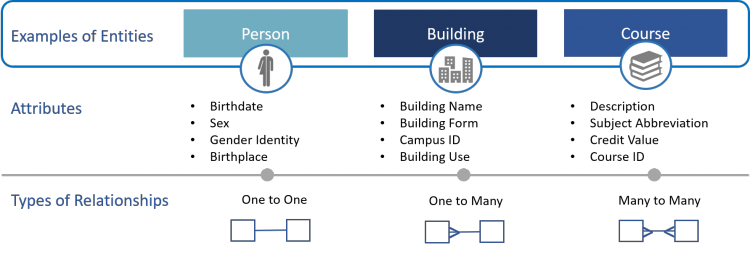
Data modeling is the process of discovering, analyzing, and scoping data requirements, and then representing and communicating these data requirements in what’s called a data model. The modeling process includes discovery and documentation of how our data fits together – its structure and definitions. Each model contains a set of components. Examples of components include entities, attributes, and relationships.
An entity is a thing about which an organization collects information about. Entities are sometimes referred to as the nouns of an organization. An entity can be thought of as the answer to a fundamental question – who, what, when, where, why, or how – or to a combination of these questions. Attributes are the details we want to record and track about entities.
University Data Model
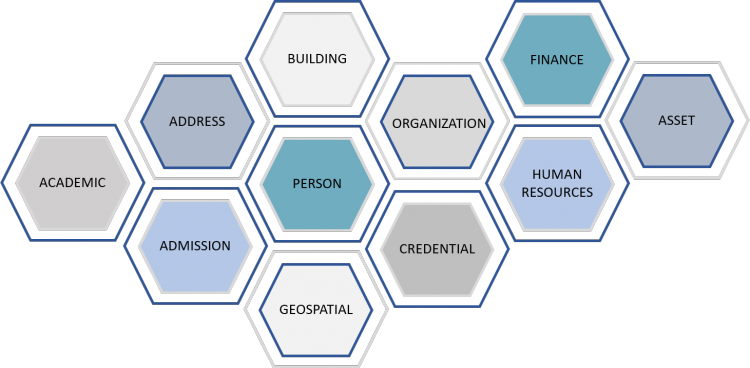
The University Data Model (UDM) is a logical representation of data (entities) and properties (attributes) of UBC’s information domains, starting at the highest-level and representing data and information required by UBC to support its processes. It also develops reports and provides a common understanding of the meaning of University data. The UDM depicts relationships, rules, constraints and semantics for key data domains, such as Person, Organization, Curriculum, and Location.
As UBC endeavors to create value from their information assets, the UDM is used to communicate data design, standards, and key relationships between entities to all participants involved throughout the data lifecycle. Since information resides in many disparate systems within UBC's Information Technology landscape and structures (e.g. files, databases, services), the need for the UDM as a tool within the information architecture framework is imperative. It will support the creation of trustworthy, consistent, and quality data.
Data Standards
A Data Standard is a rule by which data is to be described and recorded. Data standards can take different forms depending on what they describe. They can assert how a field must be populated, provide rules governing the relationships between fields, and include detailed documentation of acceptable and unacceptable values, format, and etc.
University Glossary
Words are often used differently. In addition, we tend to develop our own internal vocabulary at UBC. A glossary will ensure a common vocabulary is shared within the University. It will document data definitions, reducing ambiguity and improve communications. Definitions must be clear, rigorous in wording, and explain any exceptions, synonyms or variants.
Reference Data
Reference Data is any kind of data that is used solely to categorize, classify, or otherwise qualify or constrain Institutional data. Certain data is required across multiple business areas, processes, and systems. The University benefits if this data is shared and business units accesses the same lists. Reference Data can be defined as part of a Data Standard. The use of Reference Data helps with data quality by constraining data values, and reducing open text fields.
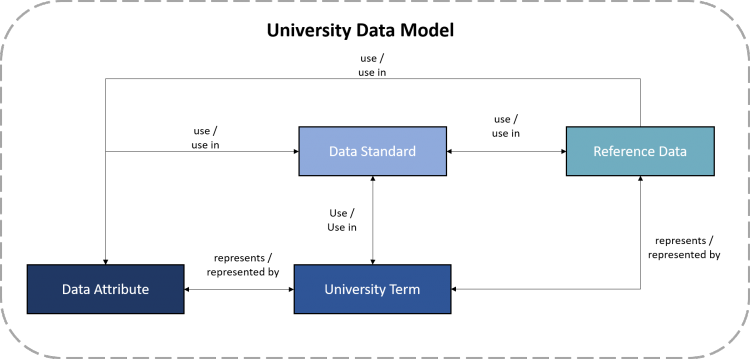
Putting it all Together
The below diagram illustrates the relationship between an attribute in the UDM and a Data Standard, Reference Data, and a University Glossary term.
UDM Data Domains
The UDM consists of the following data domains. They have been defined with consultation from working groups representing stakeholders.